Producing silicone kitchenware is essential for modern kitchens, but have you ever wondered about its environmental footprint? Understanding the production process can help us make more sustainable choices.
The production of silicone involves several stages that influence its overall environmental impact, from raw material extraction to manufacturing and recycling.
I remember researching the lifecycle of silicone kitchenware to ensure our products were as eco-friendly as possible. This journey revealed both challenges and innovations in silicone production.
What Are the Main Environmental Challenges Associated with Silicone Production?
Silicone production, while offering durability and versatility, presents several environmental challenges that need addressing to minimize its ecological footprint.
The primary environmental challenges in silicone production include resource extraction, energy consumption, and emissions during manufacturing processes.
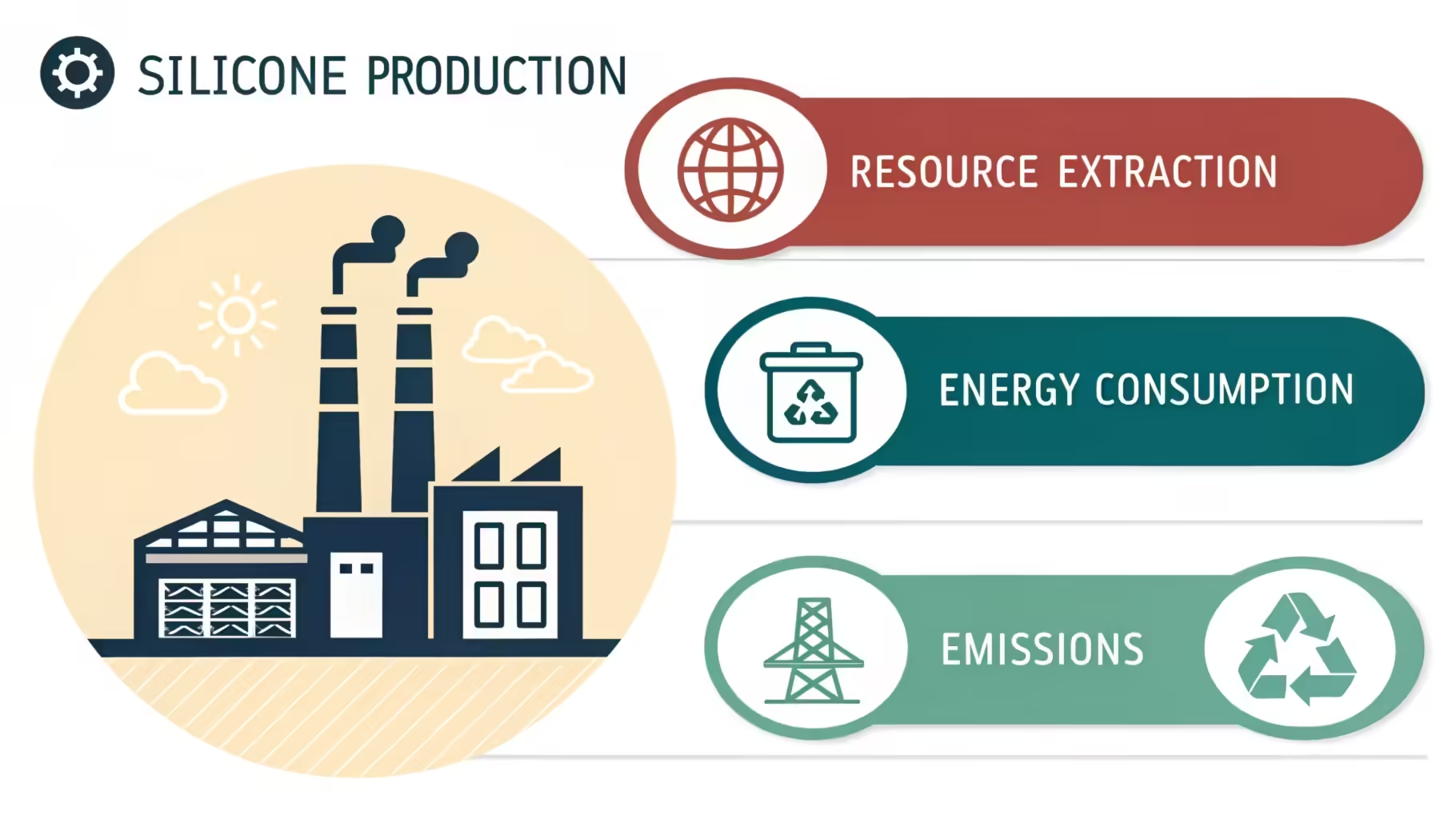
Resource Extraction
- Silica Mining: Silicone is derived from silica, which requires extensive mining. Mining activities can lead to habitat destruction and soil erosion.
- Non-Renewable Resources: While silica is abundant, the extraction process relies on non-renewable energy sources, contributing to resource depletion.
Energy Consumption
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| High Energy Use | Manufacturing silicone requires significant energy, often from fossil fuels. |
| Carbon Emissions | The energy-intensive process results in substantial carbon emissions, impacting climate change. |
Emissions and Waste
- Greenhouse Gases: The production process releases greenhouse gases, which contribute to global warming.
- Chemical Byproducts: Manufacturing silicone can produce hazardous byproducts if not managed properly.
Mitigation Strategies
- Sustainable Mining Practices: Implementing eco-friendly mining techniques can reduce habitat disruption.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Shifting to renewable energy can lower the carbon footprint of silicone production.
- Waste Management: Effective waste treatment and recycling methods are essential to minimize harmful emissions.
How Can the Energy Consumption in Silicone Production Be Reduced?
Reducing energy consumption in silicone production is crucial for minimizing its environmental impact. Several strategies can be implemented to achieve greater energy efficiency.
Implementing energy-efficient technologies and optimizing manufacturing processes can significantly reduce the energy consumption associated with silicone production.

Energy-Efficient Technologies
- Advanced Manufacturing Equipment: Utilizing modern, energy-efficient machinery can lower energy usage during production.
- Process Optimization: Streamlining production processes to eliminate energy waste and improve efficiency.
Renewable Energy Integration
| Strategy | Impact |
|---|---|
| Solar Power | Reduces reliance on fossil fuels, lowering carbon emissions. |
| Wind Energy | Provides a sustainable energy source for manufacturing facilities. |
| Energy Storage Systems | Ensures a consistent energy supply, enhancing production stability. |
Waste Heat Recovery
- Heat Exchangers: Capturing and reusing waste heat from manufacturing processes can improve overall energy efficiency.
- Thermal Energy Storage: Storing excess heat for later use reduces the need for additional energy inputs.
Case Study: Sustainable Silicone Manufacturing
One manufacturer successfully reduced its energy consumption by 20% by upgrading to energy-efficient equipment and integrating solar power into its production line. This shift not only lowered operational costs but also minimized its environmental footprint.
What Innovative Methods Are Being Developed to Make Silicone More Recyclable?
Innovation plays a vital role in enhancing the recyclability of silicone, making it a more sustainable material choice. New methods are being developed to improve the recycling process and reduce waste.
Innovative recycling techniques, such as chemical recycling and upcycling, are being explored to make silicone more recyclable and reduce its environmental impact.

Chemical Recycling
- Depolymerization: Breaking down silicone into its monomers for reuse in new products.
- Solvent-Based Processes: Using solvents to dissolve and separate silicone from contaminants, allowing for cleaner recycling.
Upcycling Initiatives
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Repurposing | Transforming used silicone into new, valuable products like mats or playground surfaces. |
| Creative Reuse | Encouraging DIY projects to give silicone items a second life, reducing overall waste. |
Closed-Loop Recycling Systems
- Manufacturer Take-Back Programs: Brands collect used silicone products for recycling, ensuring a continuous loop of material reuse.
- Collaborative Efforts: Partnerships between manufacturers and recycling facilities to streamline the recycling process and increase efficiency.
Future Prospects
Researchers are developing biodegradable silicone alternatives and enhancing the efficiency of existing recycling methods. These advancements aim to create a more sustainable lifecycle for silicone kitchenware, reducing its long-term environmental impact.
How Does the Non-Biodegradability of Silicone Impact Its Environmental Footprint?
Silicone’s non-biodegradable nature presents both advantages and challenges in terms of environmental sustainability. Understanding its impact is essential for responsible usage and disposal.
While silicone’s durability reduces the need for frequent replacements, its non-biodegradability means it can persist in the environment if not properly managed.

Long-Term Persistence
- Durability: Silicone’s resistance to degradation ensures it lasts longer but also means it remains in the environment for extended periods if not recycled.
- Waste Accumulation: Improper disposal can lead to silicone waste accumulating in landfills and natural habitats.
Environmental Impact
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Landfill Space | Non-biodegradable silicone occupies landfill space for decades. |
| Marine Pollution | Silicone items can contribute to marine pollution, harming aquatic life. |
| Resource Use | Persistent silicone waste necessitates ongoing resource extraction for replacements. |
Mitigation Strategies
- Enhanced Recycling Programs: Promoting and expanding recycling options for silicone to prevent it from entering landfills.
- Product Design for Recyclability: Designing silicone products that are easier to recycle can reduce their environmental footprint.
- Public Awareness: Educating consumers about proper disposal and recycling methods to minimize silicone waste.
Balancing Durability and Sustainability
While silicone’s longevity is a benefit in reducing frequent replacements, addressing its non-biodegradability through improved recycling and responsible disposal practices is crucial for minimizing its environmental impact.
What Are the Best Practices for Responsible Disposal of Silicone Products?
Responsible disposal of silicone kitchenware is essential to mitigate its environmental impact. Adopting best practices ensures that silicone products are managed sustainably at the end of their lifecycle.
Implementing proper disposal and recycling methods can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of silicone kitchenware.

Recycling Programs
- Manufacturer Take-Back Programs: Many manufacturers offer programs to collect and recycle used silicone products, ensuring they are processed correctly.
- Local Recycling Facilities: Identifying and utilizing local recycling centers that accept silicone can help manage waste effectively.
Upcycling and Repurposing
| Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| DIY Projects | Transforming old silicone kitchenware into new household items or craft projects. |
| Creative Reuse | Using silicone items for different purposes, such as gardening tools or storage solutions. |
Proper Disposal Methods
- Avoid Landfills: Whenever possible, avoid disposing of silicone products in landfills by opting for recycling or upcycling.
- Community Recycling Initiatives: Participating in or organizing community recycling drives can help manage silicone waste more effectively.
Educating Consumers
- Awareness Campaigns: Promoting awareness about the importance of responsible disposal and available recycling options.
- Guidelines and Resources: Providing clear guidelines and resources on how to dispose of silicone products responsibly.
Sustainable Product Design
- Modular Design: Creating silicone products that can be easily disassembled for recycling.
- Eco-Friendly Packaging: Using sustainable packaging materials to complement the responsible disposal of silicone items.
Conclusion
The production process of silicone significantly affects its environmental impact through resource extraction, energy consumption, and emissions. By addressing these challenges with energy-efficient technologies, innovative recycling methods, and responsible disposal practices, we can mitigate silicone’s environmental footprint. Understanding the balance between silicone’s durability and its non-biodegradability is key to making sustainable choices. Embracing best practices for disposal and supporting advancements in recycling can help ensure that silicone kitchenware remains a viable, eco-friendly option for the future.
